Introduction
The concept of distance and azimuth survey technique is a simple but very effective tool for geographers even with today's technology. This is because GPS can be prone to failure due to interference from large buildings and/or tree canopy over. Also there could be issues with the device itself or may have forgotten it before entering the field. Nevertheless, the distance and azimuth method is a very useful and foundational method in field work.
Methods
To begin this lab the class was divided into groups of 3 and 4 people. Each group was then to complete a survey of a set of trees on the campuses southern end, on Putnam drive. The survey would consist of gathering data on each tree such tree circumference, tree type, azimuth and distance from the origin of the survey.
The Each member of the team was given a different tool to complete the survey. The tools used were two tape measures, a range finder, survey compass, GPS receiver, and field notebook. All the measurements and other data was recorded into the field notebook so that the data could be entered into an excel file to be brought into ArcMap (fig. 3).
 | ||
Figure 1. GPS unit used to record the origin of the survey
|
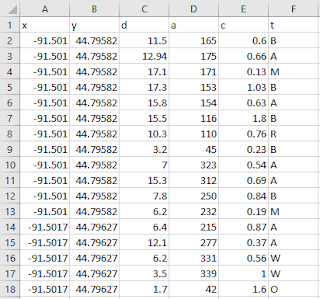 |
| Figure 3. Excel spreadsheet that has all the data collected during the survey. |
The data from the field notebook was transfered into excel. The excel spreadsheet was transfered into a newly created file geodatabase. Using the Bearing Distance to Line tool was used to give the data its azimuth and the Feature Vertixes to Points tool was used to create the individual points for each of the trees.
Results
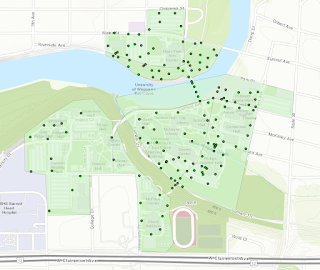
The first step in evaluating the accuracy of the survey was to visually inspect the accuracy of the GPS location. Qualitatively the accuracy of the GPS appears to be accurate (fig. 1). The survey taken on to the west may be slightly off to the north. This was likely caused by poor GPS signals from tree cover and the adjacent hill located to the south. The map created below (fig. 1) shows the tree type for each of the trees collected within the surveys. When comparing the results of the surveys there is more homogeneity between the tree species in the western survey compared to the survey taken to the east.
 |
| Figure 4. Map created in ArcMap that displays the location and tree type for each of the trees within the survey. The locations of the trees was determined by taking the azimuth each of the trees and measuring the distance from the origin. |
The distance and azimuth survey method is a very effective method for data collection in the field. By taking the distance and azimuth of objects from a single point of origin, accurate spatial data can be taken in the field even without the aid of more sophisticated technology such as GPS.